Text to Speech and Speech to Text are two powerful AI technologies that convert language between written and spoken forms.
Text to speech converts written words into audio that you can listen to, making digital content more accessible and interactive.
Speech to text works in reverse, instantly converting spoken words into readable text, improving productivity and real-time communication.
Although both use artificial intelligence, they serve different needs: text-to-speech helps you listen to written text, while speech-to-text helps you write down what you speak.
Together, these tools are transforming how we interact with devices, enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and user experience across many everyday applications and industries.
What Is Text to Speech?
Text to Speech is an AI technology that converts written text into natural sound.
This technology helps businesses, creators, and educators convert blogs, emails, and scripts into audio, improving accessibility, engagement, and communication across websites, apps, videos, and digital products around the world today.
What Is Speech to Text?
Speech to Text is an AI-powered technology that listens to spoken words and instantly turns them into written text, helping businesses, creators, and users capture ideas, commands and conversations.
Differences Between Text to Speech(TTS) and Speech to Text (STT)
Text to Speech (TTS) and Speech to Text (STT) are AI-powered technologies that bridge spoken and written language, enabling seamless communication between humans and machines.
|
Feature |
Text to Speech (TTS) |
Speech to Text (STT) |
|
Function |
Converts written text into spoken words |
Converts spoken words into written text |
|
Technology |
Uses AI voice synthesis |
Uses AI speech recognition |
|
Input |
Text |
Audio / Voice |
|
Output |
Audio / Speech |
Text |
|
Use Cases |
Audiobooks, virtual assistants, accessibility tools |
Transcription, voice commands, real-time captions |
|
Advantages |
Enhances accessibility, improves engagement, personalized voice options |
Saves time on manual typing, enables voice-driven interfaces, improves productivity |
|
Challenges |
Naturalness of voice, pronunciation accuracy |
Accents, background noise, homophones |
Functionality
TTS transforms written content into audible speech, while STT captures spoken words and converts them into written form.
Technology Used
TTS relies on natural language processing (NLP) and voice synthesis, whereas STT uses speech recognition algorithms and AI to detect words.
Input and Output
TTS requires text input and produces speech output, ideal for listening experiences. STT takes voice input and produces textual output, perfect for documentation.
Applications
TTS is widely used in audiobooks, virtual assistants, and accessibility tools for visually impaired users. STT is critical for transcription services, real-time captions, and voice-controlled applications.
Advantages
TTS enhances user engagement and accessibility, providing a personalized audio experience. STT boosts efficiency, allowing hands-free documentation and faster content creation.
Challenges
TTS may struggle with natural intonation and pronunciation, whereas STT can be impacted by accents, speech clarity, and background noise.
Text-to-speech and speech-to-text are transforming the way we interact with computers, making digital communication faster, easier, and more accessible for everyone.
How Text to Speech Works?
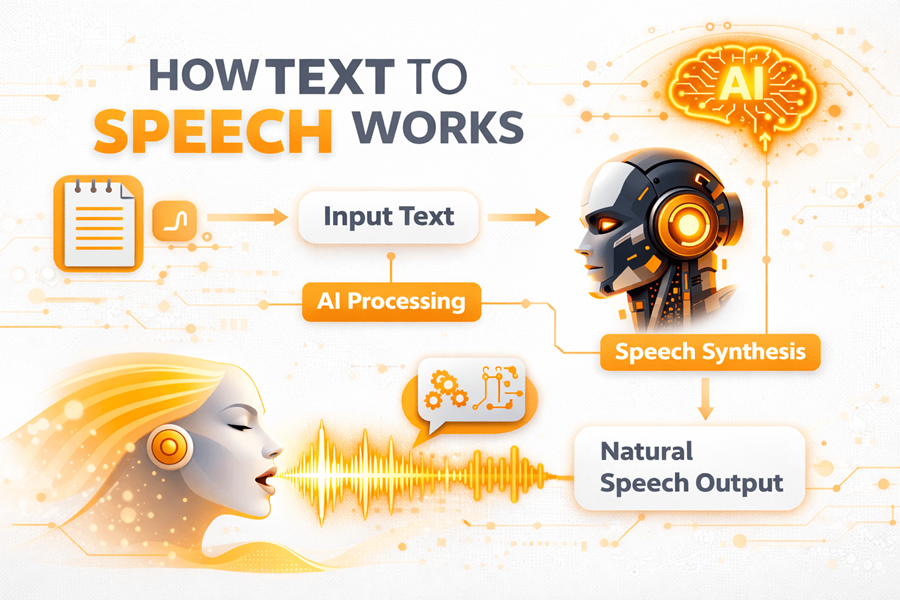
Text to Speech (TTS) transforms digital text into clear, human-like audio, making information accessible, improving communication, and enhancing user experiences across devices and applications.
- Input Analysis: Examines text for punctuation, context and ensuring correct pronunciation and tone.
- Linguistic Processing: Converts words into phonemes applying rules for natural speech.
- Voice Synthesis: AI transforms phonemes into audio with human-like voice quality.
- Customization Options: Users choose voices, accents, and speeds for personalization.
- Integration: TTS embeds into apps, websites and devices for communication.
How Speech to Text Works?
Speech to Text lets devices listen and turn spoken language into readable text by analysing audio patterns and language logic.
- Capture Audio: A microphone or device records your voice, turning sound into a digital signal.
- Digitise Sound: The raw audio is converted from analog waves into digital data for processing.
- Feature Analysis: Algorithms break the sound into small units (phonemes) that represent bits of speech.
- Match Language Patterns: Machine learning models compare phonemes to words using language rules and context.
- Generate Text: The system compiles recognised words into a written transcript you can read or edit.
Text to Speech and Speech to Text Use Cases
Text to Speech and Speech to Text are essential AI‑driven technologies that convert written text into natural audio and spoken language into text respectively, enhancing accessibility, communication, and productivity across industries.
Text to Speech Use Cases:
- Accessibility for visually impaired users on websites and apps.
- Voice assistants provide spoken responses.
- Audiobooks and e‑learning narration.
- Automated voiceovers in marketing and videos.
- Customer service IVR systems.
Speech to Text Use Cases:
- Dictation and voice typing in apps.
- Transcribing meetings, interviews, and lectures.
- Real‑time captions for events or calls.
- Voice commands for devices and smart assistants.
- Accessibility for users with mobility or reading challenges.
Conclusion
Reading about text-to-speech and speech-to-text makes it clear that these AI technologies are shaping communication.
In 2026, businesses, educators, and creators can use TTS and STT to improve accessibility, engagement, and productivity across apps, websites, and devices.
Adopting these tools enables faster content creation, real-time interaction, and inclusive experiences, making digital communication smarter and more efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
-

Krishna Handge
WOWinfotech
Dec 25,2025